Troubleshoot pod issues
Detect issues
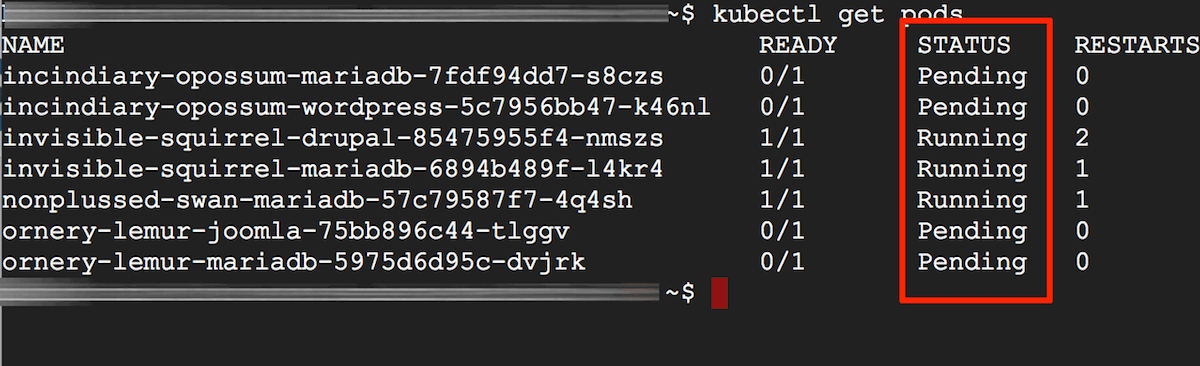
To check if the status of your pods is healthy, the easiest way is to run the kubectl get pods command. After that, you can use kubectl describe and kubectl logs to obtain more detailed information.
Solve issues
Once you run kubectl get pods, you may find your pods showing any of the following statuses:
- Pending or CrashLoopBackOff
- ImagePullBackOff or ErrImagePull
Pod status is Pending or CrashLoopBackOff
If you see any of your pods showing a Pending or CrashLoopBackOff status when running the kubectl get pods command, this means that the pod could not be scheduled on a node.
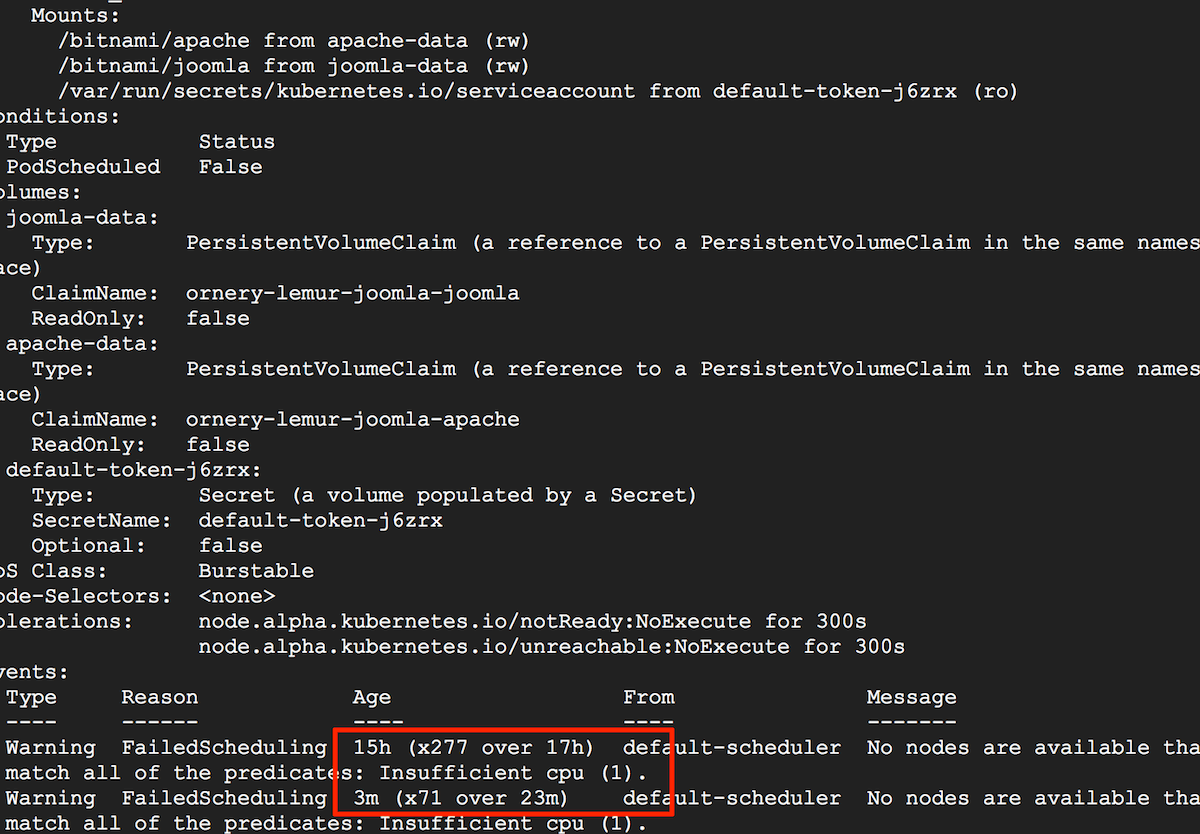
Usually, this is because of insufficient CPU or memory resources. It could also arise due to the absence of a network overlay or a volume provider. To confirm the cause, note the pod identifier from the previous command and then run the command below, replacing the POD-UID placeholder with the correct identifier:
$ kubectl describe pod POD-UID
You should see an output message providing some information about why the pod is pending. Check the example below:
If available resources are insufficient, try the following steps:
-
Option 1: Add more nodes to the cluster. Check out the documentation of the chart you have installed to learn how to add more nodes to the cluster.
-
Option 2: Free up existing cluster resources by terminating uneeded pods and nodes. To do so:
-
Confirm the name of the node you want to remove using kubectl get nodes and make sure that all the pods on the node can terminate without issues (replace NODE-NAME with the name of the node you want to terminate):
$ kubectl get nodes $ kubectl get pods -o wide | grep NODE-NAME -
Evict all user pods from the node:
$ kubectl drain NODE-NAME -
Now you can safely remove the node:
$ kubectl delete node NODE-NAME -
Free up the cluster by terminating uneeded deployments. First check the name of your releases using the helm list command and then, delete the uneeded deployment (replace RELEASE-NAME with the name of the release you want to delete):
$ helm list $ helm delete RELEASE-NAME
Pod status is ImagePullBackOff or ErrImagePull
When your pod status is ImagePullBackOff or ErrImagePull, this means that the pod could not run because it could not pull the image. To confirm this, note the pod identifier from the previous command and then run the command below, replacing the POD-UID placeholder with the correct identifier:
$ kubectl describe pod POD-UID
The output of the command will show you more information about the failed pull. Check that the image name is correct and try pulling the image manually on the host using docker pull. For example, to manually pull an image from Docker Hub, use the command below by replacing IMAGE with the image ID:
$ docker pull IMAGE